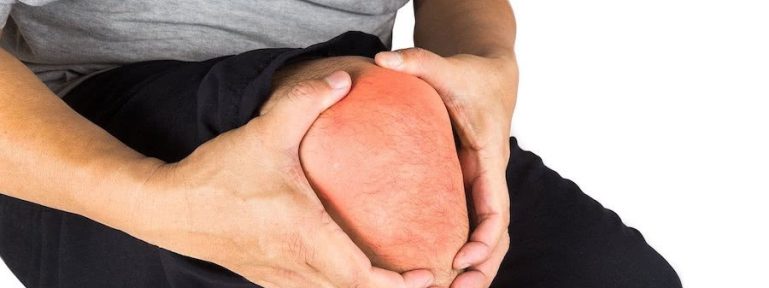
Yes, in most cases, it can be really painful! The human knee is a key joint that allows us to walk, run and move. But put too much stress or load through it, and it can suffer from various conditions that can lead to discomfort and stiffness. One such condition is the buildup of fluid in the knee, medically referred to as 'knee effusion' and commonly known as 'water on the knee'. Can fluid on the knee cause pain? The straightforward answer is yes, it can.
Symptoms of Fluid on the Knee
Symptoms of fluid on the knee typically involve two things:
- Knee pain
- Knee stiffness (especially when bending the knee)
Other symptoms and signs may include:
- Redness
- Heat
- Tender to touch
- Difficulty straightening the leg
- Visible swelling or bulges
Swelling
One of the most noticeable symptoms of knee effusion is swelling. The affected knee may appear larger, puffier, or swollen and will likely feel rather painful compared to the other knee. Sometimes the skin around the knee can become taut, making it visibly clear that there is an accumulation of fluid.
Swelling is often related to inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by degeneration (e.g. in the case of arthritis), trauma, and injury.
Pain
Knee effusion can cause both acute and chronic pain. Acute pain is typically sharp and occurs short term, often due to an injury. Chronic pain, on the other hand, is persistent and may result from long-term conditions like osteoarthritis.
Knee pain can be bad when putting pressure through it (e.g. walking or running), or when moving it (if you try to bend it), or when being still (e.g. in bed).
Pain during rest might indicate chronic inflammation or severe injury, while pain during activity often points to mechanical issues or acute injuries. Both types of pain can significantly impact daily life and mobility.
Sensation of Pressure and Irritation
Individuals with fluid buildup in their knee often report feeling pressure within the joint. This sensation arises from the swelling exerting a hydrostatic pressure or force on surrounding tissues and structures within the knee. The increased pressure can cause irritation leading to discomfort even when at rest. Some people describe this feeling as having a "squishy" or "spongy" texture upon touching the swollen area.
Stiffness
Stiffness in the knee joint affects daily movements by reducing flexibility, especially when bending the knee, and often when straightening the knee too.
If you lose knee bend, you lose the majority of the function of the knee. That means that putting on socks, climbing stairs, or even getting in and out of a car can be painful.
Similar to bending, straightening the knee can also be problematic in some individuals. The fluid buildup restricts full extension, causing discomfort and difficulty especially in bed.
Movement Impairment
One issue occurs when the knee pain becomes chronic, and muscle atrophy (degeneration of the muscles around the knee) can occur. This leads to weakness, and this further exacerbates the issue.
People may adopt a limp or shift their weight to the other leg to minimise pain, which can lead to further musculoskeletal and compensatory issues. Changes in walking pattern, or gait, are common in those with knee effusion and after a while that can cause issues with the foot, hip, and most commonly the lower back.
Long-term functional impairment is a significant concern for chronic knee effusion. Without proper management, the condition can lead to permanent changes in joint structure and function.
Knee Locking and Clicking
Knee effusion can sometimes cause mechanical symptoms like clicking, popping, or locking sensations during movement. These occurrences happen when inflamed tissues interfere with normal joint mechanics causing momentary "catches" or disruptions in smooth motion. Occasional locking episodes where you temporarily lose ability to move your knee freely can be particularly concerning requiring prompt medical attention.
Instability
Instability can cause the knee to give way unexpectedly, increasing the risk of falls and further injury. This is less common, but can occur, and is often caused by pain on weight bearing.
Instability impacts mobility by causing uncertainty in movements, making it difficult to perform weight-bearing activities with confidence. This can lead to a more sedentary lifestyle and reduced physical health.
Temperature
Warmth around the affected knee is a common sign of inflammation. This temperature change can be felt by comparing the affected knee to the non-affected knee.
The degree of warmth may or may not correlate with the intensity of pain. Higher temperatures could suggest higher levels of inflammation, but not always.
Redness
Redness indicates an inflammatory response and is often accompanied by swelling and pain. It can be a sign of infection, such as septic arthritis, or other inflammatory conditions.
How Fluid on the Knee Causes Pain
Mechanisms of Pain in Knee Effusion
The mechanisms of pain in knee effusion include increased pressure within the joint, inflammatory responses, and the impact on nerve endings. These factors combine to cause knee pain and discomfort.
Pressure on Surrounding Structures
Excess fluid causes pressure on the surrounding structures of the knee joint, including muscles, ligaments, and tendons. This pressure can lead to significant pain and difficulty moving the knee.
Inflammatory Responses
Inflammatory responses in the knee joint result from conditions like arthritis or infection. These responses lead to the production of pro-inflammatory substances that cause pain and swelling.
Impact on Nerve Endings
The excess fluid and inflammation can irritate nerve endings in the knee, causing pain signals to be sent to the brain. This irritation can lead to chronic pain and discomfort.
Chronic vs. Acute
Chronic pain in knee effusion is persistent and often associated with long-term conditions like arthritis. Acute pain, on the other hand, is sudden and severe, typically resulting from injuries.
Patterns and Triggers
Understanding pain patterns and triggers is crucial in managing knee effusion. Pain can be triggered by specific movements, activities, or even at rest, depending on the underlying cause.
Seeking Medical Attention
Persistent or severe pain, significant swelling, fever, and inability to bear weight on the knee are signs that require prompt evaluation and we suggest you go to A&E.
Less severe pain, when you are feeling generally well, would be a good indication to see us for a knee aspiration (or injection).